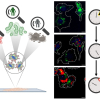
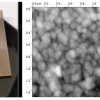
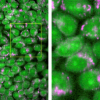
Tests at Rice University’s Brown School of Engineering of a two-dimensional Janus compound showed it could be an effective and universal platform for improving the detection of biomolecules via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Using glucose to test the material proved its ability to boost its Raman enhancement factor by more than 100,000 times, which the researchers say is comparable to the highest-reported enhancement factor for 2D substrates.
Metallic SERS media often prompt side reactions that create background noise. Janus MoSSe synthesised at Rice University is non-metallic. “This work mainly addresses whether we can enhance the target molecules’ signal strength”, said materials scientist and principal investigator Jun Lou. “We wanted to know if we could make it stand out from the background noise.”
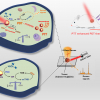
MoSSe introduced by the Lou lab in 2017 was produced by chemical vapour deposition. Molybdenum sits in the middle with a layer of sulfur on one side and another of selenium on the other; hence the two-faced Janus characterisation. The different electronegativities of each layer make it a SERS “superstar”, said lead author and Rice alumnus Shuai Jia, a former graduate student in Lou’s lab.
“The dipole created between the top sulfur and the bottom selenium lands out-of-plane, and this creates an electrical field a few nanometres beyond the MoSSe”, Jia said. That field interacts with molecules that come close, enhancing their vibrational intensity enough to be detected.
The researchers noted tests with MoSSe also detected molecules of the neurotransmitter dopamine and that the substrate should be adaptable to sense other molecules.
Lou said that there is room for improvement. “We’re looking at hybrids of MoSSe with some metallic nanoparticles, and also trying to enhance the dipole strength”, he said.
This work is reported in Nanoscale (http://doi.org/dvt7).