Raman Spectroscopy News
Princeton Instruments has appointed ROSH Electroptics as their exclusive sales representative in Israel.
Nanostructure-based lenses provide focussing and dispersion, and allow smaller devices with increased functionality.
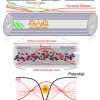
A new approach has been shown to decrease the emission linewidth from a molecule; one of the key aims in precision spectroscopy.
A new interpetation of Raman spectra enables biological carbon to be distinguished from other sources.
Raman spectroscopy sensor can determine which tissue layer an epidural needle is in and ensure correct delivery of the anaesthetic.
Entries for the IRDG Chalmers and Dent Student Travel Award for a PhD to present their research at the SciX meeting.
A technique to combine the ultra-sensitivity of surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) with a slippery surface invented by researchers at Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, will make it feasible to detect single molecules of a number of chemical and biological species from gaseous, liquid or solid samples.
A surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) method is to be used to study pesticides on and their penetration into fresh intact produce.
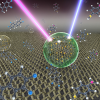
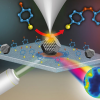
Scientists at EPFL have shown how a light-induced force can amplify the sensitivity and resolution of SERS for the study of single molecules.
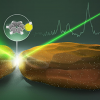
A team of researchers has demonstrated a new type of imaging system based on Raman spectroscopy that reveals the chemical composition of living tissue for medical diagnostics and cellular studies.
Horiba Scientific has announced that Francis Ndi, current Export Manager, has been promoted to Product Line Manager for the Optical Spectroscopy Division (OSD).
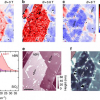
Using Raman spectroscopy and statistical analysis, an international group of scientists has succeeded in taking nanoscale measurements of the strain present at each pixel on the surface of graphene. The researchers also obtained a high-resolution view of the chemical properties of the graphene surface.
Kidney stones rank among the most common illnesses. Their recurrence may be prevented with the right post-operative care. However, for this to be effective, the composition of the stones needs to be known. Fraunhofer researchers are developing a Raman spectroscopy based system for rapid analysis of urinary stones immediately after the surgical procedure.
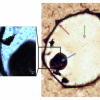
The National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in the UK has used tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy to map catalytic reactions at the nanoscale for the first time.
Rand Capital Corporation has invested $250,000 as part of a $4.3 million equity capital funding round in SciAps, Inc., manufacturer of handheld analytical instruments. The funding round was led by new investor Jolimont Global Mining Systems with participation from Rand Capital, and other existing investors including SciAps CEO and Founder Donald Sackett, as well as two additional new investors.
Renishaw recently broke ground on its new 133,000 ft2 office and warehouse facility in West Dundee, IL, USA, about 40 miles from Chicago. The two-storey facility will be located at the Oakview Business Park and will be the company’s North American headquarters. The new building, planned to be ready in June 2016, will also include space for product development, testing, warehousing and distribution. The facility will consolidate the company’s two existing sites and can also accommodate future expansion.
A clinically approved assay system based on surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy has been launched by Renishaw Diagnostics.
Canadian researchers have used SERS to screen blood samples for molecular traces that indicate the presence of precancerous polyps in the colon, a key warning sign for colon cancer. Their results may yield a cheaper and less invasive initial screening test for colon cancer that could complement colonoscopy, though further clinical trials will need to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of the blood test before it is routinely used.
Raman microscopy is being used alongside high-resolution X-ray diffraction to unpick the reasons for crystallographic defects in SiC bulk crystal and epitaxial film, which limit the commercialisation of SiC devices.