Articles
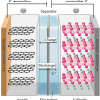
Lithium ion batteries power most of the electrical devices we rely on every day. As well as mobile phones, laptops and tablets, they are finding increasing use in vehicles, with electric cars not uncommon on our streets. This article is from a young scientist who has won help for her research through an instrument company’s support programme. You can find out more, read the article and even apply yourself.
The study of metabolites in our sewage systems is not new, but there are particular difficulties with identifying the metabolites from new psychoactive substances, or “legal highs”. The authors describe a wide range of sample collection methodologies and their analysis with mass spectrometry.
Concentrations of therapeutic drugs and their metabolites in waste and surface water are measured by highly selective and sensitive mass spectrometric techniques, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). Using data obtained in this way, information about human metabolism of single active principles, and WWTPs characteristics (e.g., flow rate, population served), it is possible to calculate the environmental loads of therapeutic drugs and correlate them to their effective use (known from sales or production data). We will consider here the analytical aspects involved in the measurements of illicit drugs and their metabolites in wastewater samples by HPLC-MS/MS.